Language Identification: ISO 639-3 eng
Other Names: English (Canada), English (Ireland), English (Jamaican), English (New Zealand).
Local name: English
Pronunciation: [ˈɪŋɡlɪʃ]
Region: British Isles; English speaking world
English is spoken in approximately 60 Sovereign states across the world
Ethnic Population: Anglo-Saxons
English users: L1 speakers: 360–400 million (2006); L2 speakers: 750 million;
as a foreign language: 600–700 million
Language family: Indo-European; Germanic; West Germanic; Anglo-Frisian; Anglic
English
Early forms: Old English; Middle English; Early Modern English
Language Status: Official language in the United Kingdom, United States of America, United Kingdom, Canada, Australia, New Zealand, South Africa, Rep of Ireland, and across another 23 countries is spoken as the primary language.
Dialects
English American; Anguillian, Antiguan, Australian, Bahamian, Bajan, Bay Islands, Belizean, Bermudian, Brunei, Burmese. Cameroonian, Canadian, Caribbean, Falkland Islands, Fijian, Gambian, Guyanese, Ghanaian, Indian, Irish, Jamaican, Kenyan, Liberian, Malawian, Malaysian, Manx, Namlish, Nepali, New Zealand, Nigerian, Pakistani, Philippine, San Andrés–Providencia, Scottish, Singapore, South African, South Atlantic, Sri Lankan, Trinidad and Tobagonian, Ugandan,Welsh.
Typology: The order of words in English is SVO (Subject – Verb – Object).
Writing system: Latin script (English alphabet)
Description of the English Language
English belongs to the Western group of the Germanic branch of the Indo-European language family.Today, English is the third most popular mother tongue in the world (after Chinese Mandarin and Spanish), with an estimated 350-400 million native speakers. it is considered, however, the largest language in the world if we consider the speakers of the second, third and higher languages. This is due first to the colonial influence of the British Empire, but later to the spread of American culture It is also a lingua franca of the world for all non-English speakers in the fields of business, science, aviation, computing, education, politics and entertainment (and many others).
Largest English speaking countries include; the USA, the UK, Canada, Australia, New Zealand and the Republic of Ireland. England is the home of the English Language. English is the mostly used language across the world, with an estimated 1 to 2 Billion people speaking English as a second language. Many Colonial countries speak English or a dialect of English.
History
The English language developed from a West German Language which was first spoken in Anglo-Saxon England in the 5th century and was later referred to as the ‘Old English’. A couple of hundred years later, the 7 century seen the introduction of Latin, this new version of English begun to replace the Anglo-Saxon and was the beginning of Latin Based English and in 1011 recorded 24 Latin letters and 5 English letters. This existed through until the 15th century until the new Modern English language began to emerge, this consists of the 26 letters we still use today.
Old English: The term Old English comes from the term Angles (Englas), 5th century, hence Old English did not represent much of the English current spoken, many speakers of English today would only understand or recognise a few word.
Middle English: The new form of English came about around 1066, 11th century, and was introduced after William the Conqueror took over England, this led to the further development of and Middle English became Modern English as we know today.
Modern English: This Modern English continued to change and be modified by taking in new words from other languages, such as French, Portuguese, Dutch, Spanish and a few other nationalities. Therefore, is the third phase of change to adapt the English Language: Old English, Middle English changing constantly through to the Early Modern English. This Early Modern English being very much influenced through a substantial change to pronunciation.
Geographical distribution
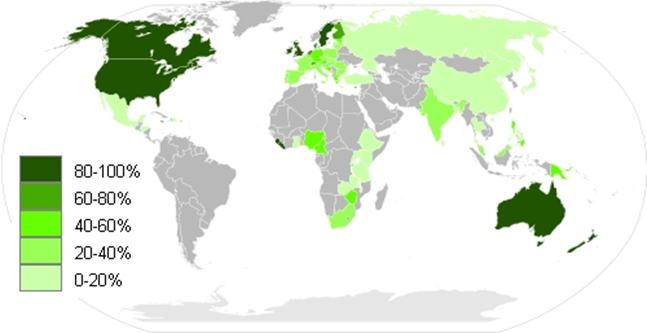
The English language is widely spoken in many corners of the world, there are 5 main countries that make up the core of English language speakers, United States of America, the United Kingdom, Canada, Australian and New Zealand (this accounts for approximately 333 Billion English Speakers as their 1st language, English is also the primary language to another 935 Billion from other countries and territories, with approximately 4.8 Billion speakers in south Africa. English is also considered the diplomatic language of the world.
Breakdown of English Language speaking nations
United States (64%), United Kingdom (16.6%), Canada (5.3%), Australia (4.7%), South Africa (1.3%), Republic of Ireland (1.3%), New Zealand (1.3%) and Other (5.5%).
The official status of English
In many countries, where English is not the most spoken language, it is still recognised as the official language, and other countries where English is a co-official language, this is mainly due to the influence of both English and American Colonisation in many parts of the world. This is reinforced through English in America, the widest speaking English country with no official language, although English is the official language in 32 of the 50 American states. Furthermore, even though America has no official language, to complete American Nationalisation you must complete a basic English Language proficiency test. Also, although not given the official Language status, English is recognised across several former colonies as an important and need to know Language; i.e. the United Arab States, Cyprus, Bahrain and Bangladesh.
Dialects
English has numerous dialects, it is estimated there are 160 English dialects across the world, a large number in England and the United Kingdom (the four nations of the UK) have a wide array of dialects (different from an accent) and across America, overall, the English language dialects are many around the world. Within the English Language, there are, as mentioned, different dialects of English, and many have different words or grammar.
British English is known as the traditional English, and is the common language dialect of English as spoken in the UK. The major dialects of English can be distributed amongst three main categories, the British Isles, North America and Australasia. In England alone it is recognised to be more than 36 dialects, and this number increases significantly across the other 3 nations of the UK.
Overall English has also been a mixed and unusual language, derived from Germanic from around 1500 years ago it has developed a widely spoken mixed bag of dialects. A blend of 7 other languages, English, German, French, Greek, Russian Welsh and Sanskrit. This increasingly mixed language, through the influence of various terms from politic, foodstuffs, animals and other inputs from migrant speakers to towards the 160 or so variety of English dialects spoken around the world.
Spoken and literary varieties
The two most common forms of standard English language spoken and used as ‘English as a Second Language’ is British English and North American English. These are used as the model of comparison of other varieties of the spoken English. Varieties include; British English (UK), Canadian English, Australian English, New Zealand English, South African English and Indian English. Within the variety of the named English Language we have a further breakdown; Pidgin English, Creole English, Regional dialect, Minority dialect and Indigenised varieties. The variety of the language increases due to the influence of the language being used in around 160 different countries.
It is said that the purest form of the English variety is spoken in Somerset, Wiltshire and Gloucestershire from the Anglo-Saxon influence. Other varieties come along due to various geographic locations, those from a specific group, academic, industrial, this is known as variations to the standard English language. Hence variations in English is influenced through the level of English required, Professional, Literary, Conversational, even Slang and Ethnic English, all are seen as a variety of the English Language.
Written language
The English language was first spoken around the 5th Century and was first written in Anglo-Saxon and brought to England by Anglo-Saxon settlers, this was dubbed as Old English. In the 7th Century Latin was introduced and begun to replace much of the Anglo-Saxon, although both were used in conjunction for a number of years, this influenced the new Latin Based English. In 1011 a monk recorded the traditional order of the Old English Alphabet comprising of 24 letters of the Latin alphabet with an additional 5 English letters. Over the years various borrowing took place until the 14th – 15th Century the new Modern English began to take shape. In the 16th Century the English language and English Alphabet now encompassed 26 letters which we still use today.
Modern English follows after Old English and Middle English and is seen as the third stage in the development of the English Language, dating from approximately 1450 to Present Day. Over this period the English Language has changed considerable in both importance and perception and is currently ranked as the number one spoken language across the world. The increase use of the English Language across Britain and Ireland, and the further spread across the Colonies of North America and the Caribbean added to the number of English speakers.
The English Alphabet
Today the English Alphabet consists of 26 letters, each letter has both an Uppercase and Lowercase representation, the English alphabet was created around the 7th century, and was derived from Latin, over the centuries letters have been added and removed which now gives us the English Alphabet consisting of the 26 letters.
In the Modern English Language, we have 21 Consonants and 5 Vowels, written from right to left. The phonology (phoneme) of the English Language varies across the number of different dialects, thus sounds vary from dialect to dialect. The number of generally recognised consonant phonemes is 24 and for the vowels there is a far greater variation which leads to approximately 21 to 25 variations in Modern English, however this number is less in both American (14 to 16) and Australian English (19 to 20).
Consonants
As previously mentioned there are 21 Consonants and 24 Consonant phonemes (basic speech sound attached to the vowel to form the syllable) used in the various English Language dialects. The 21 basic speech consonants of the English consists of:
Three of the most commonly used English language consonants are R, S and T, and most of the time a single consonant will represent a single sound, although there are a number of commonly used 2 and 3 letter consonants which can represent a different sound.
| Aa [eɪ] | Bb [biː] | Cc [siː] | Dd [diː] |
| Ee [iː] | Ff [ɛf] | Gg [dʒiː] | Hh [eɪtʃ] |
| Ii [aɪ] | Jj [dʒeɪ] | Kk [keɪ] | Ll [ɛl] |
| Mm [ɛm] | Nn [ɛn] | Oo [oʊ] | Pp [piː] |
| Qq [kjuː] | Rr [ɑː] | Ss [ɛs] | Tt [tiː] |
| Uu [juː] | Vv [viː] | Ww [ˈdʌbəl juː] | Xx [ɛks] |
| Yy [waɪ] | Zz [ziː] |
English Cardinal Numbers
| 1 one | 2 two | 3 three | 4 four |
| Ee [iː] | Ff [ɛf] | Gg [dʒiː] | Hh [eɪtʃ] |
| 5 five | 6 six | 7 seven | 8 eight |
| 9 nine | 10 ten | 11 eleven | 12 twelve |
| 13 Thirteen | 14 fourteen | 15 fifteen | 16 sixteen |
| 17 seventeen | 18 eighteen | 19 nineteen | 20 twenty |
TYPOLOGICAL DESCRIPTION
The order of words in English is SVO (Subject – Verb – Object). This is known as a VO language where the Verb comes before the Object and is typical in around 58% of used Language’s. In this construct of a sentence the Subject come first, followed by the Verb and the Object making up the latter part of the sentence..
In English the use of SVO is seen as relatively inflexible as it tends to identify the part of the sentence which is recognised as the subject, which is followed by the object. (John walked the dog), the SVO is sometimes seen as a simpler than other modes of Typology such as (VSO or VOS) sentence construction. Although the English language is seen as SVO it still contains traces or SOV which is embedded in German, and Dutch, which influenced the Old English language.
Grammar
English words and grammar are commonly identified through nouns, determiners, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, prepositions and conjunctions, these are World Classes or Parts of Speech of English (ways in which member words combine), these are further split, Nouns forming the largest class and Verbs form the second largest class.
Noun
Commonly used to identify a class of persons, place or thing (common noun), or a proper noun when used to name a particular person, place or thing. A word that mainly functions as the name of a specific thing or group of things, animals, creatures, objects, actions, places, ideas or a state of existence. A noun is a participant of the open part of speech which can occur as the main word in a sentence, words that can occur with articles and adjectives and can work as the head of a phrase.
There are several ways to classify nouns In English grammar. One way is whether they are countable or uncountable nouns. Countable nouns, as the term suggests, are things that can be counted. They have singular and plural forms. In contrast, uncountable nouns cannot be counted. They have a singular form and do not have a plural form. Gender is not marked, but is preserved in 3rd person pronouns. There are no cases, but possession is expressed by the clitic –s, e.g., mother’s. There is a definite and an indefinite article.
Pronouns
Pronouns are words that can sometimes function as a noun, and can be used independently or on behalf of the noun. In the English language we have several kinds of pronouns; these are not exhaustive and can include: Personal, Demonstrative, Interrogative, Indefinite, Possessive and Reciprocal pronouns. A simple definition of a pronoun is I, me, she, he, you, they, that, whoever, whatever, someone, etc. The pronoun can take the place of the noun, example; John saw his father and he shouted, the pronoun ‘he’ takes the place of John.
Prepositions
Prepositions are words that tell where something is or when something is happening, commonly used words include; before, after, behind, beside, between, above, under, at, in, out, down, off, on, towards, etc.
Adjectives
Adjectives are known to transform a noun or a noun phrase, the role of the adjective is to amend the information presented by the noun. Adjectives are the main a ‘part of speech’ within the English language. A main function of the adjective is to enhance and define the noun or the pronoun. An adjective is basically to help describe things, the Green (adjective) Apple, the description of the Apple (noun). They provide enhancement to the English language. Adjectives may be found in three positions in an English sentence: before a noun (a nice girl); as a complement, after a verb (the school is open); after a noun or an indefinite pronoun (is there anyone interested in the class?).
Verbs
Verbs are words that describe something, an action or description of something that has happened. English verbs are more complex than nouns, they are marked for the following categories: in the 3rd person, e.g., he/she/it stands.
There are three voices: active, passive and middle There are four moods: declarative, imperative, conditional, and subjunctive. Most English verbs express tense/aspect through the use of various combinations of the auxiliary verbs be and have + main verb. Like all Germanic languages, English has regular verbs that add –ed to form the past tense, e.g., listen – listened, and irregular verbs that undergo internal vowel changes e.g., come – came. Interrogative constructions use the auxiliary verb do.
References
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/English-speaking_world#Countries_where_English_is_an_official_language
https://simple.wikipedia.org/wiki/English_alphabet
http://www.ello.uos.de/field.php/EarlyModernEnglish/TheStatusOfTheEnglishLanguage
